FINLAND’S EDUCATION SYSTEM
Thursday - 18/12/2025
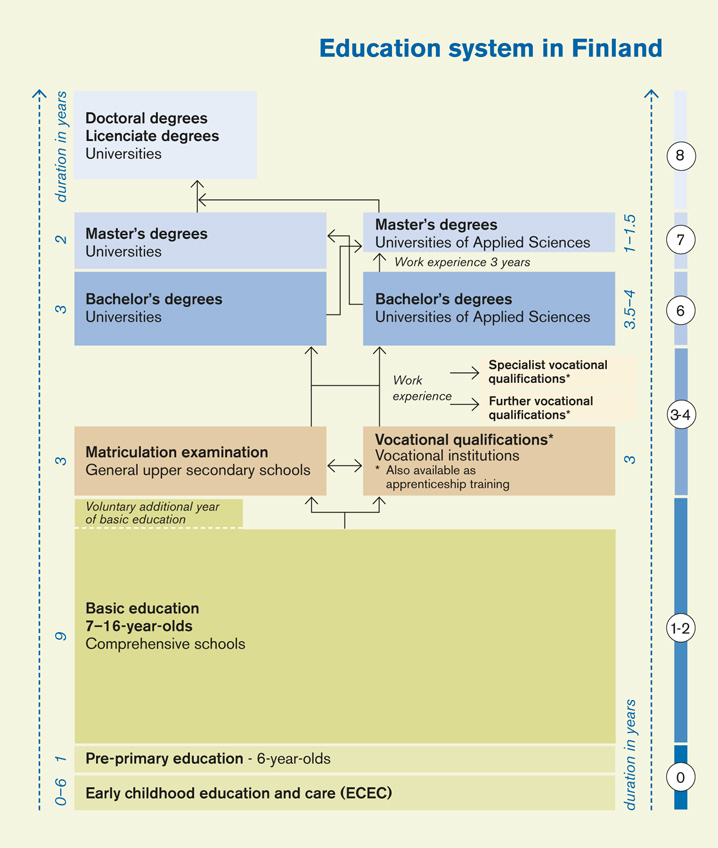
The education system in Finland is completely free of charge for Finnish citizens and is divided into the following levels:
- Early childhood education and care (non-compulsory): for children aged 0-5;
- Pre-primary education (non-compulsory): 1 year, for children aged 6;
- Compulsory basic education: lasts 9 years, for students aged 7-16. This is the only compulsory level of schooling for Finnish students (equivalent to primary and lower secondary education). Students attend comprehensive schools: during the first 6 years, each class is taught by one main teacher (except for arts and skills subjects), and during the final 3 years, students are taught by subject-specific teachers (e.g., Mathematics, Science, etc.).
Education after completing grade 9 (age 16) is voluntary. Finland does not place heavy emphasis on pushing students toward university but instead balances pathways between academic higher education and vocational training.
- Upper secondary education: lasts 3 years (ages 17-19), and students can choose between two options:
- General upper secondary schools: prepare students for the national matriculation examination (the Finnish Matriculation Exam), suitable for academically strong students who wish to continue to higher education;
- Vocational qualifications: offered at vocational institutions, providing training in various occupational fields.
- Higher Education (Universities and Universities of Applied Sciences): consists of two parallel sectors – universities and Universities of Applied Sciences (UAS).
- Universities: focus on academic research and advanced education related to research, offering Bachelor’s, Master’s, postgraduate diplomas, and Doctoral degrees;
- Universities of Applied Sciences (UAS): focus on professional and practical training with strong links to working life, suitable for students who wish to enter the workforce soon after graduation. These institutions award professional Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees, after which students may continue to doctoral studies.
For tailored guidance and full assistance throughout your study-abroad journey, please contact:
Duc Anh EduConnect
Hotline: 09887 09698
Email: duhoc@ducanh.edu.vn
Website: www.ducanhduhoc.vn