Australia’s Education System
Thứ Bảy - 29/11/2025
This section covers: How the Australian education system works, Australia’s qualification framework, education policies, and levels of study.
1. How Does the Australian Education System Work?
Each state and territory in Australia independently manages its school and vocational education systems, including both public and private institutions. This includes responsibility for:
- Funding and budgeting
- Policies and regulations
- Curriculum development
- Quality assurance
- Day-to-day management and operational matters
Because each state/territory governs its own system, specific details may vary, but the overall quality of education across Australia remains consistently high.
The Australian Government oversees universities, providing funding and establishing national education standards. Universities develop their own curriculum, policies, operations, and development plans – all within the framework of national education regulations.
For further information on education in each Australian state and territory, please refer to: Canberra, New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, Western Australia and Northern Territory.
2. The Australian Qualifications System
Australia has 17 nationally recognized qualification types across three education sectors:
- School education (Secondary)
- Vocational Education and Training (VET)
- Higher Education (University)
For full details, you may refer to the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF) here. Below is a summary of how Australia’s qualification framework is structured:
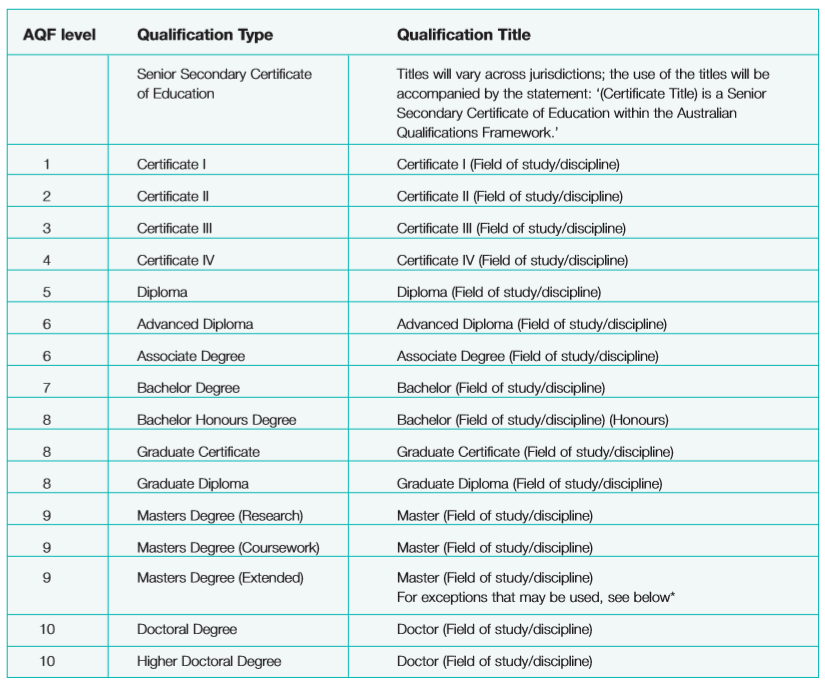
3. Education Policies in Australia
Australia has several important education policies designed to protect international students. These are essential for students and parents to understand when considering study in Australia:
- The Education Services for Overseas Students (ESOS) Act 2000: The ESOS Act is a fundamental national law that governs Australia’s international education sector. It regulates:
- The registration and operation of education providers
- Financial management and protection of student tuition fees
- Legal compliance requirements for schools and institutions
- Quality assurance and integrity of Australia’s education system
- Alignment with Australian immigration policies
The ESOS Act ensures the quality, safety, and reputation of Australian education, while safeguarding international students’ rights and financial interests.
- The National Code of Practice for Providers of Education to Overseas Students: This national code outlines the standards that education providers must follow when delivering programs to international students. It covers four main areas:
- The legislative framework
- Regulatory bodies and their responsibilities
- Standards for program registration
- Requirements and obligations for education providers
This code ensures that institutions deliver high-quality education, provide adequate support, and meet national standards in all aspects of international student management.
- The Commonwealth Register of Institutions and Courses for Overseas Students (CRICOS): CRICOS is a national registry that lists:
- All institutions approved to teach international students
- All programs/courses that are officially registered for overseas students
Each institution and each course is assigned a unique CRICOS code. Only programs listed on CRICOS are eligible for student visa applications. See more information here.
4. Levels of Study in Australia
Including: School Education, Vocational Education, and Higher Education
School Education (Primary & Secondary)
Australia’s school system spans 12 years, divided into:
- Primary School
- Junior Secondary (Lower Secondary)
- Senior Secondary (Upper Secondary)
Students receive two key qualifications during their schooling:
- Year 10 Certificate
- Senior Secondary Certificate of Education (Year 12 Certificate) – known by different names depending on the state or territory.
From Year 10 onwards, Australian students may study both secondary school subjects and vocational courses simultaneously (a combined academic–vocational pathway).
After completing high school, students may choose to:
- Enter the workforce
- Continue vocational training at Certificate or Diploma levels
- Progress to university study
Some secondary schools also offer university foundation programs, often linked directly to specific university degrees.See the list of Australian high schools here.
Vocational Education and Training (VET)
Australia’s vocational colleges offer training across a wide range of industry sectors and issue the following nationally recognized qualifications:
- Certificate I – typically 3 to 6 months
- Certificate II & III – typically 6 to 12 months
- Certificate IV – typically 1 year
- Diploma – typically 1 to 2 years
- Advanced Diploma – typically 2 to 2.5 years
- Vocational Graduate Certificate – typically 6 months
- Vocational Graduate Diploma – typically 1 to 1.5 years
Australia has:
- Over 60 public vocational institutions known as TAFE (Technical and Further Education)
- Around 5,000 private vocational colleges
- Approximately 95% of Australian high schools offering vocational education through Vocational Training Centers on campus.
Tuition fees for VET programs generally range from AUD 9,000 to 14,000 per year.
See more information about VET institutions here.
Higher Education (University Level)
Australia has 39 public universities, 2 private universities, and one U.S.-affiliated university campus located in South Australia.
Australian universities operate campuses both within Australia and in several other countries, and many have partnership programs with domestic and international universities.
In addition to universities, Australia also has numerous government-recognized higher education institutions and institutes that deliver accredited higher education programs.
See the list of Australian universities here.
If you need support, contact us here.
Duc Anh EduConnect
Hotline: 09887 09698, 09630 49860
Email: duhoc@ducanh.edu.vn
Website: ducanhduhoc.vn/






