EDUCATION SYSTEM IN GERMANY
Thứ Ba - 16/12/2025
Germany is home to one of the world’s highest-quality education systems and was ranked the 4th best country to live in according to the 2019 US News & World Report survey.
In Germany, students can choose to study:
- In German – offered at all public universities (tuition-free) and private schools (tuition-based);
- In English – offered at selected public universities and most private institutions (tuition-based).
1. Preschool Education
Preschools in Germany are operated mainly by churches or non-profit organizations and focus on childcare services. The system is divided into several groups:
- Kinderkrippe: for children aged 8 weeks to 3 years;
- Kita: for children aged 3 to 6, open from 7 AM to 5 PM;
- Kindergarten: for children aged 3 to 6 (half-day or full-day);
- Hort/Schulhort: after-school care for primary school students.
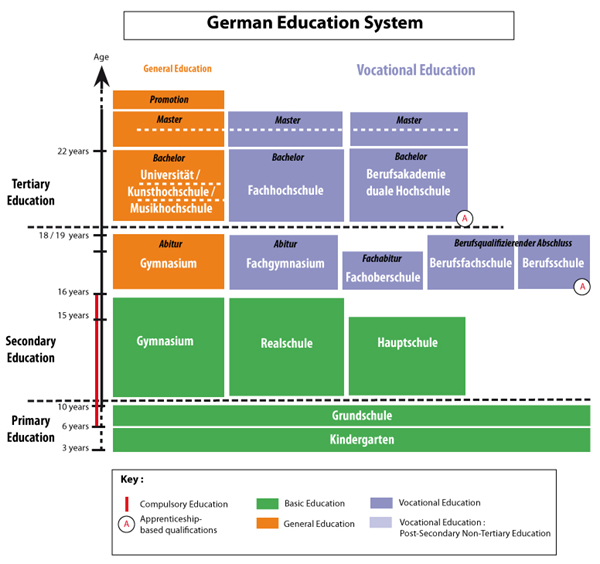
2. Primary Education
At age 6, children enter primary school (Grundschule), which lasts 4 years, except in Berlin and Brandenburg where it lasts 6 years. Most schools begin the academic year in September.
3. Secondary Education
Upon completing primary school (typically at age 10, or 12 in Berlin/Brandenburg), students move into one of five secondary school pathways:
- Hauptschule (Grades 5-9 or 5-10): The least common track in Germany, suitable for students aiming for vocational or industrial careers. Students receive basic vocational preparation and often work part-time as trainees. After a final exam in Grade 9 or 10, most transition to Berufsschule (vocational school) for 2 years;
- Realschule (Grades 5-10): Chosen by about 40% of German students annually. This track is similar to the U.S. middle-high school model and provides a balanced academic foundation;
- Mittelschule (Grades 5-10): A combined pathway featuring both vocational and academic elements (a hybrid of Hauptschule and Realschule);
- Gymnasium (Grades 5-12 or 5-13): For academically strong students aiming for university studies. The curriculum is theory-intensive, requiring two foreign languages and advanced coursework in mathematics and sciences;
- Gesamtschule (Grades 5-12 or 5-13): A comprehensive state school combining elements of the above three pathways.
4. Higher Education
a. Vocational Schools (Berufsschule) – 2 to 3 years: Although not formally part of the public education system, Berufsschule is heavily supported and regulated by the federal government. It combines classroom instruction with vocational training. Students usually enter after completing Realschule or Mittelschule.
b. Higher Education Institutions: As of 2013, Germany had 427 higher-education institutions, including 6 teacher-training colleges, 17 theological schools, 52 colleges of art, 215 universities of applied sciences (Fachhochschulen), 20 state-run training institutes. Less than 100 are private institutions.
Germany’s higher-education landscape includes:
- Universities (Universitäten): Focused on academic and theoretical instruction. All programs are research-based and follow the principle of “unity of research and teaching”. These institutions form the core of Germany’s traditional higher education system;
- Universities of Applied Sciences (Fachhochschulen): Practice-oriented programs that emphasize hands-on learning, professional skills, and industry relevance. Programs are structured and optimized for shorter study periods (typically 4 years). Graduates are highly employable, as many German and international companies prefer candidates with strong practical skills.
For tailored guidance and full assistance throughout your study-abroad journey, please contact:
Duc Anh EduConnect
Hotline: 09887 09698
Email: duhoc@ducanh.edu.vn
Website: www.ducanhduhoc.vn







